Monte Carlo Variance Reduction Research & Code Developing & Nuclear Engineering
Prev ….. Next
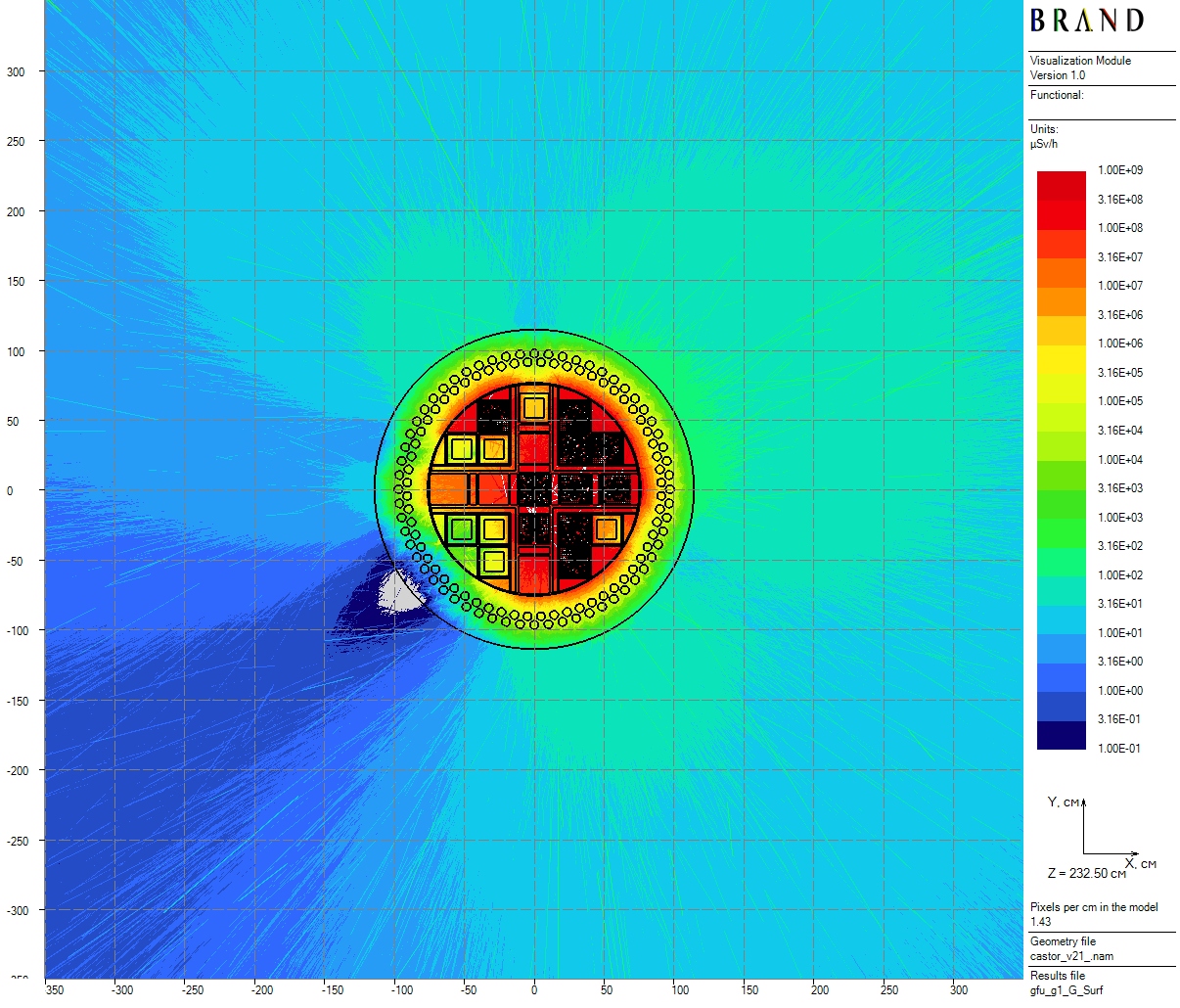
CASTOR-V/21 spent fuel cask
The following asymmetrical load of the CASTOR-V/21 fuel cask [1] is considered below:
- 10 spent $15 \times 15$ PWR fuel assemblies of 3.11 wt.% initial enrichment, 35.7 GWd/MTU burn-up, and 46 months cooling time;
- 7 quadratic combined absorbers which consist of two coaxial polyethylene and lead prisms of inradius 7 cm and 10.5 cm respectively;
- 4 empty positions.
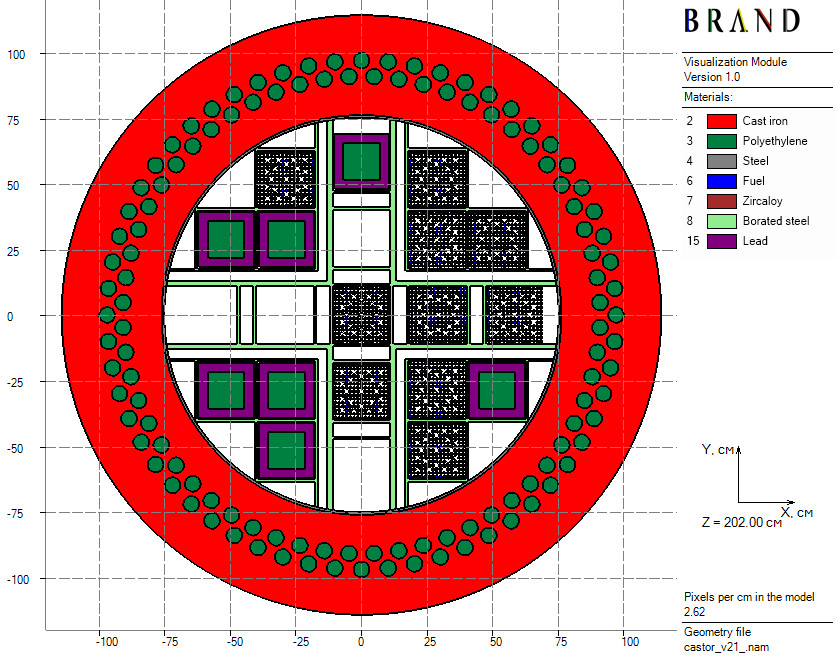 |
| Figure 1: Horizontal cross-section of the loaded cask |
In these calculations, the following techniques are used:
- Expected value estimators;
- Joint location-direction importance sampling from source (for primary gamma only);
- Energy importance sampling from source (for primary gamma only);
- Exponential transform;
- Prohibition of leakage (for the skyshine problems);
- Simplified adaptive splitting.
The primary computational gain is achieved here thanks to the simplified adaptive splitting, exponential transform (for both gamma), and prohibition of leakage (for the skyshine problems) techniques.
Computed flux functional - ambient equivalent dose H*(10) [2] rates.
Several computations cases results are provided:
- Single cask (total running time - 13.5 hours);
- Additional calculation for the single cask side surface primary gamma dose rates distribution (total running time - 25.2 hours);
- The cask is located in the center of $10^5$ cm air sphere inside a hypothetical labyrinth-like absorbing either polyethylene or lead construction which is designed for domination of the skyshine effect in radiation transfer (total running time - 12.6 hours);
- The same as above model but the construction has an air-filled perforation of 100 cm radius on 2500 cm height above the cask bottom (total running time - 12.7 hours).
Below, the results of the neutron-gamma and gamma problems computations are presented (see details in [3]).
Neutron results
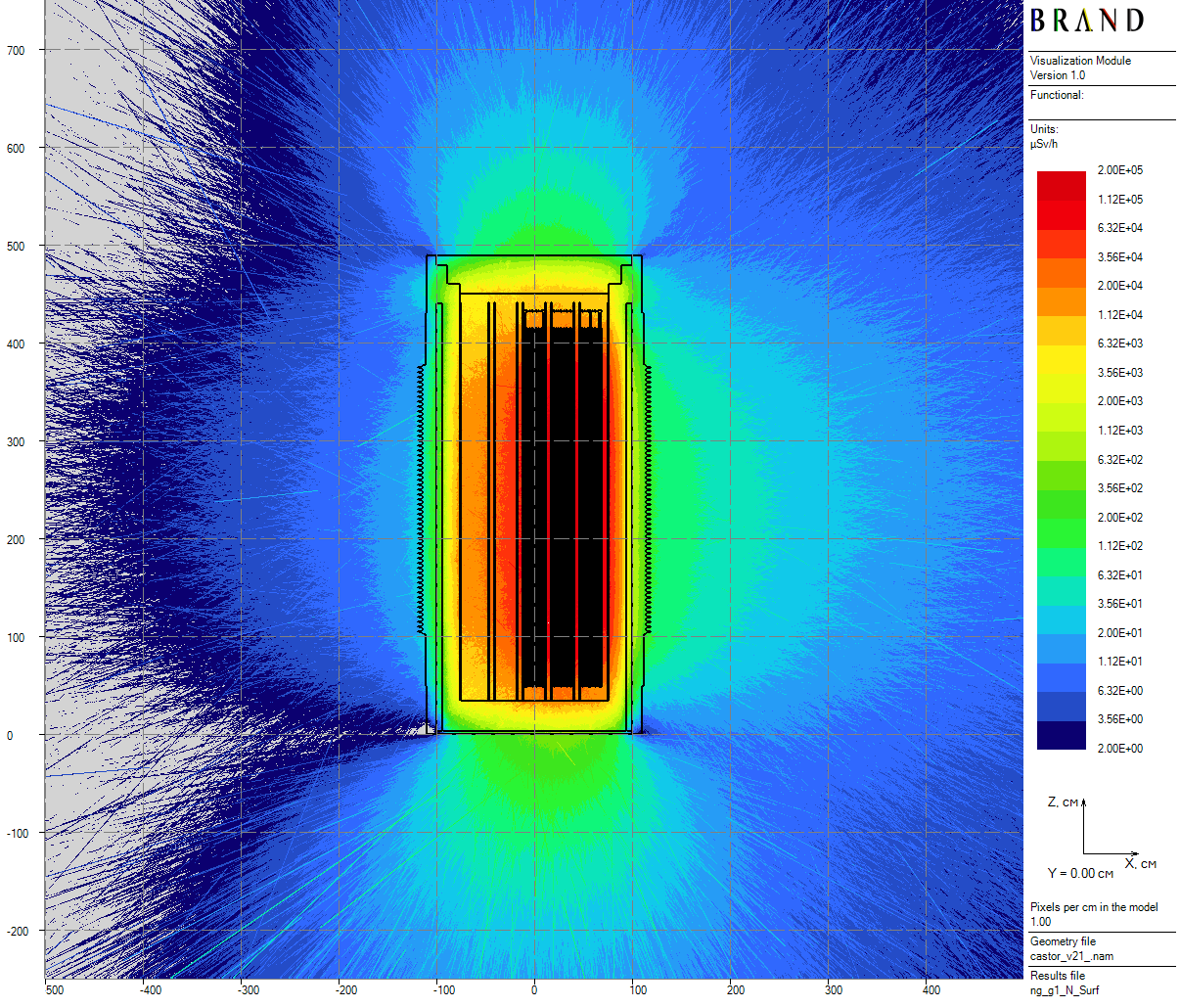 |
| Figure 2: Neutron axial dose rates distribution for the single cask (20 cm thick) |
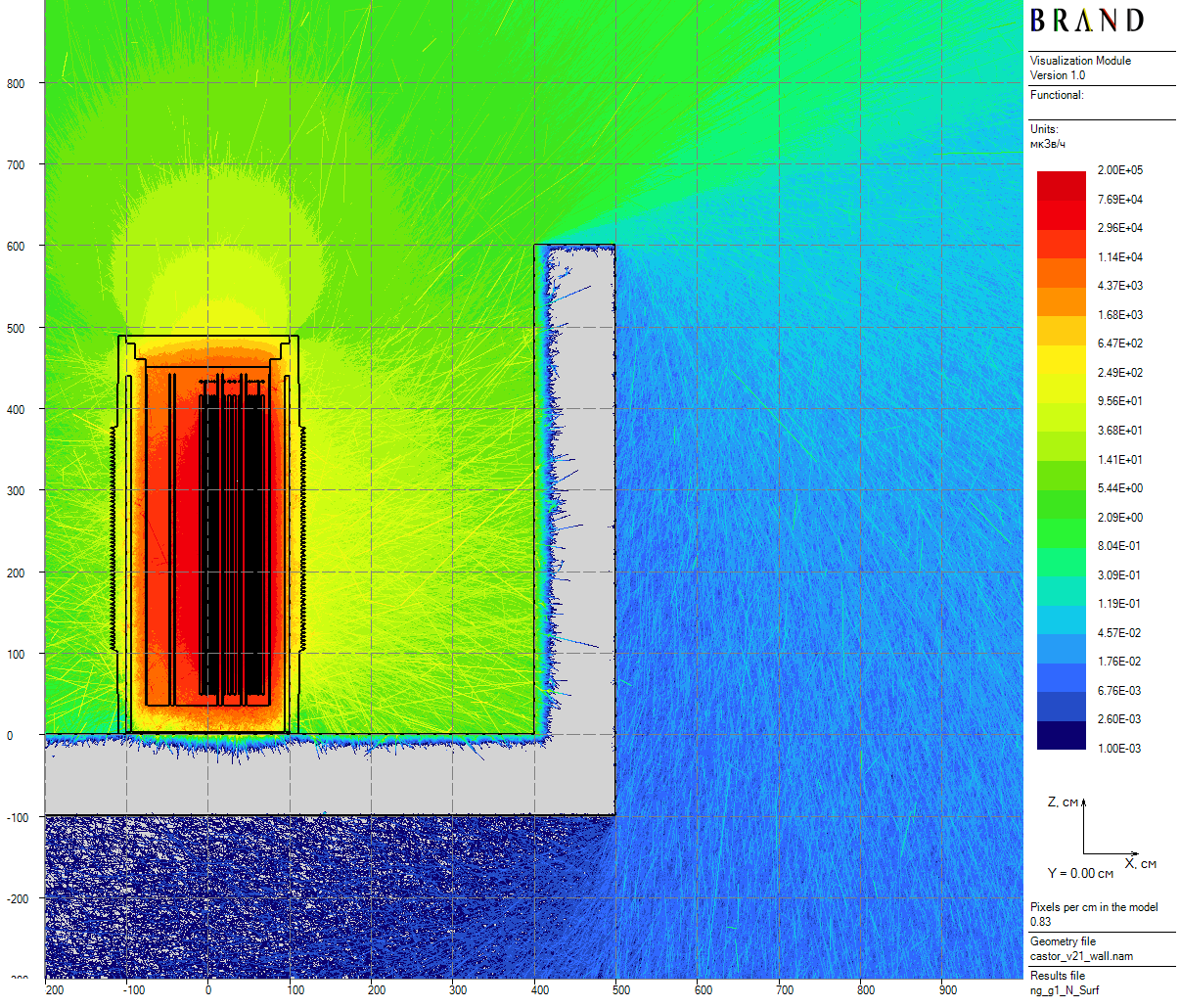 |
| Figure 3: Neutron vertical dose rates distribution for the cask in the skyshine model (20 cm thick) |
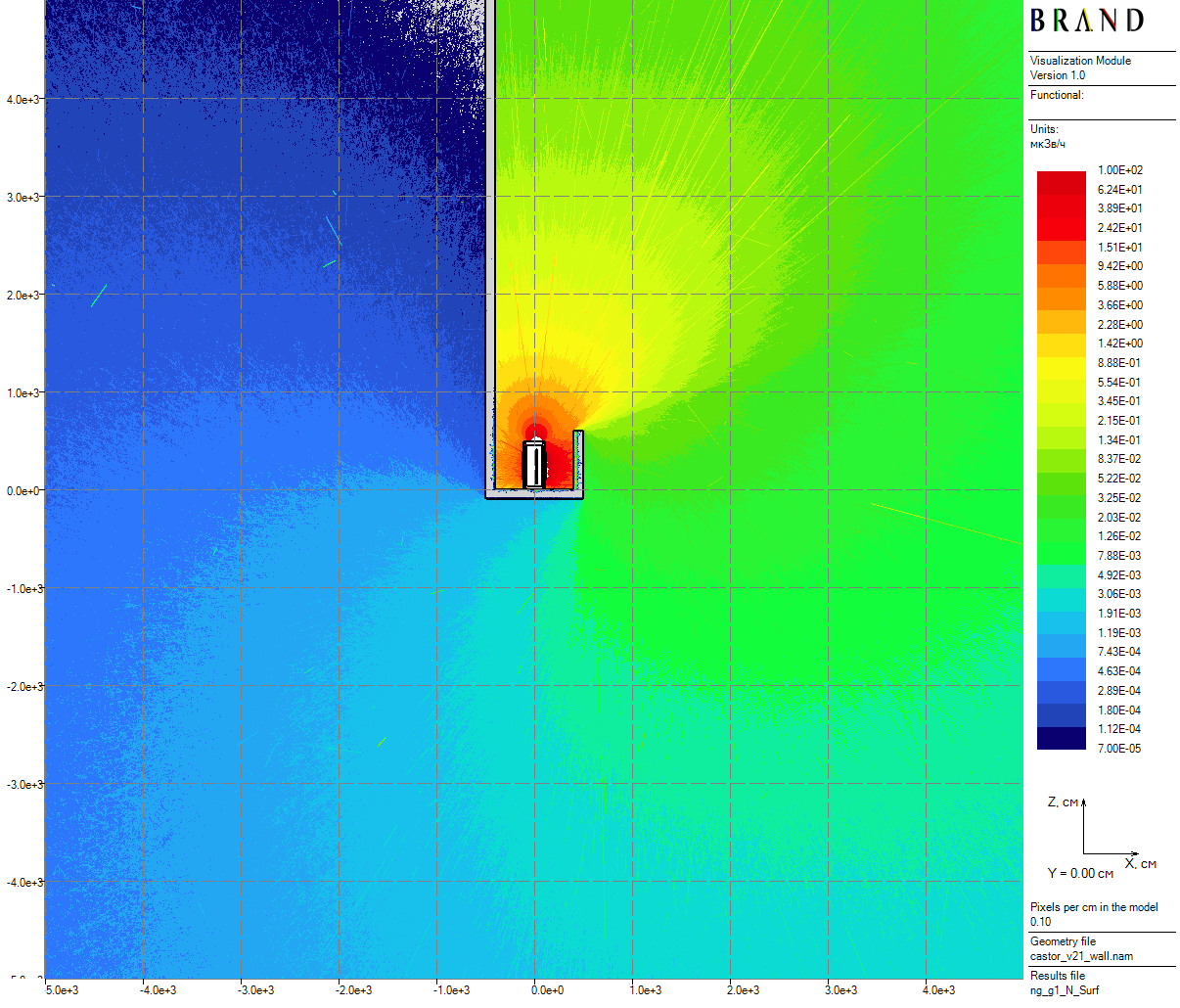 |
| Figure 4: Neutron vertical dose rates distribution for the cask in the skyshine model (100 cm thick) |
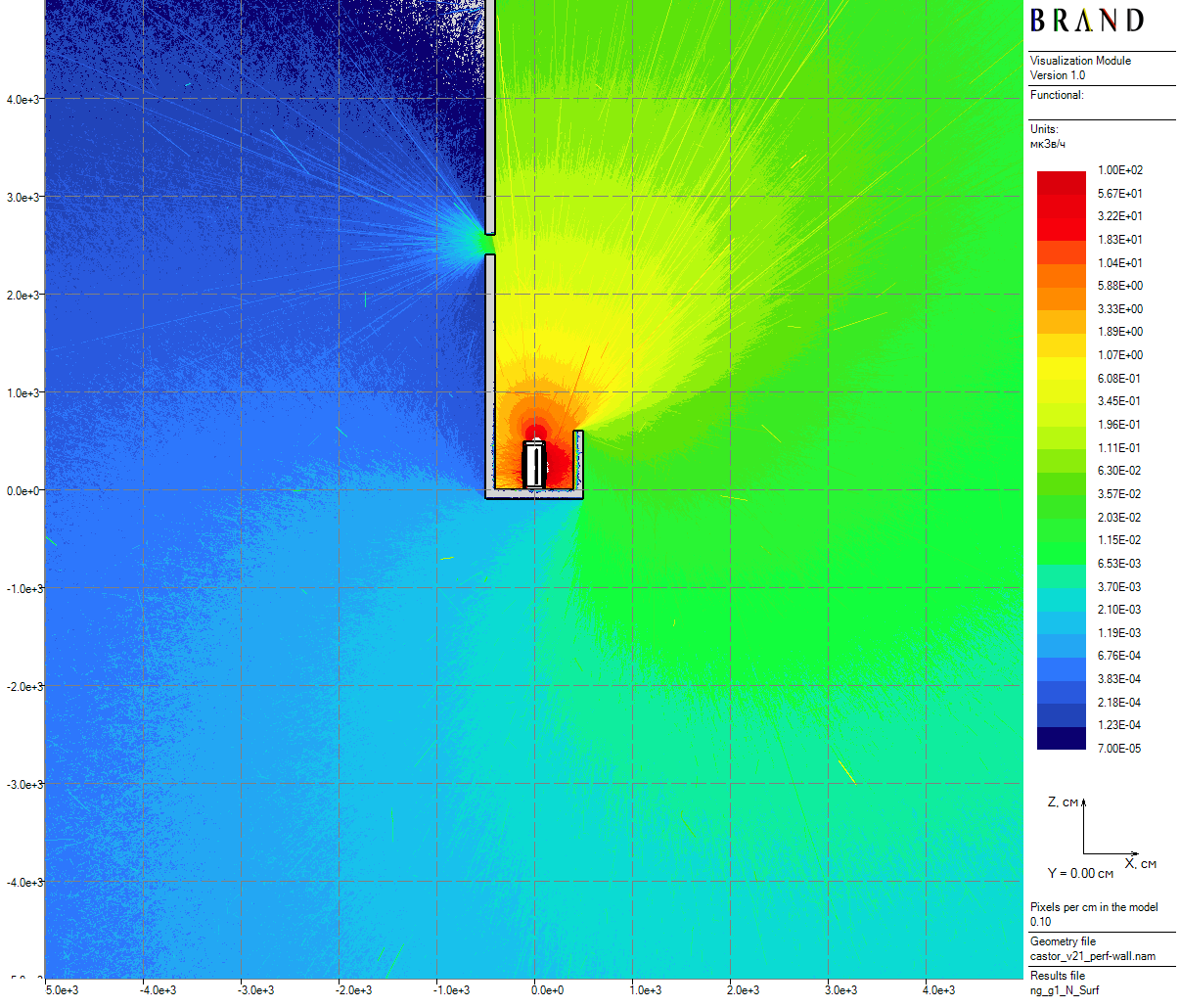 |
| Figure 5: Neutron vertical dose rates for the cask in the skyshine model with the perforation (100 cm thick) |
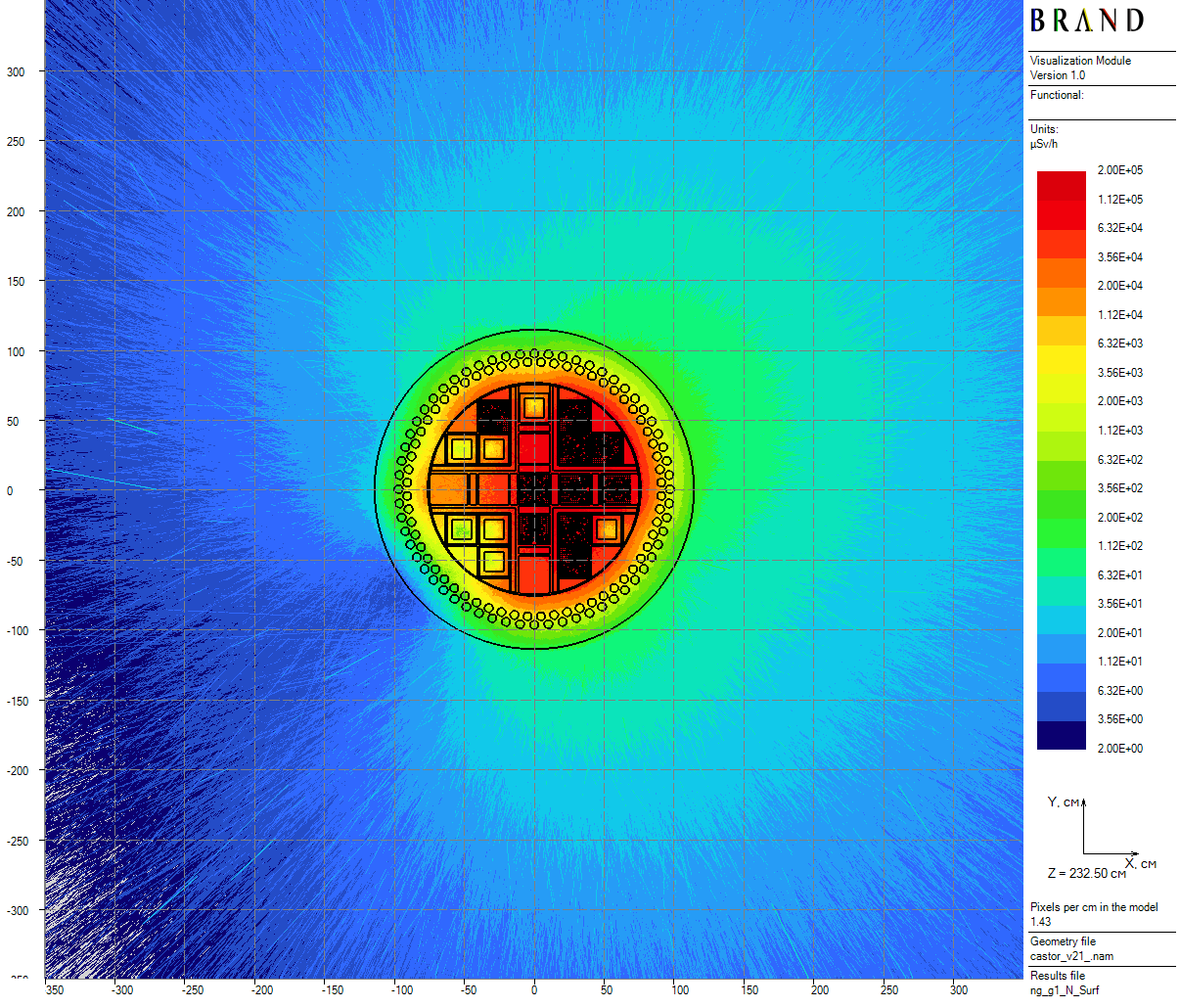 |
| Figure 6: Neutron azimuthal dose rates for the single cask (20 cm thick) |
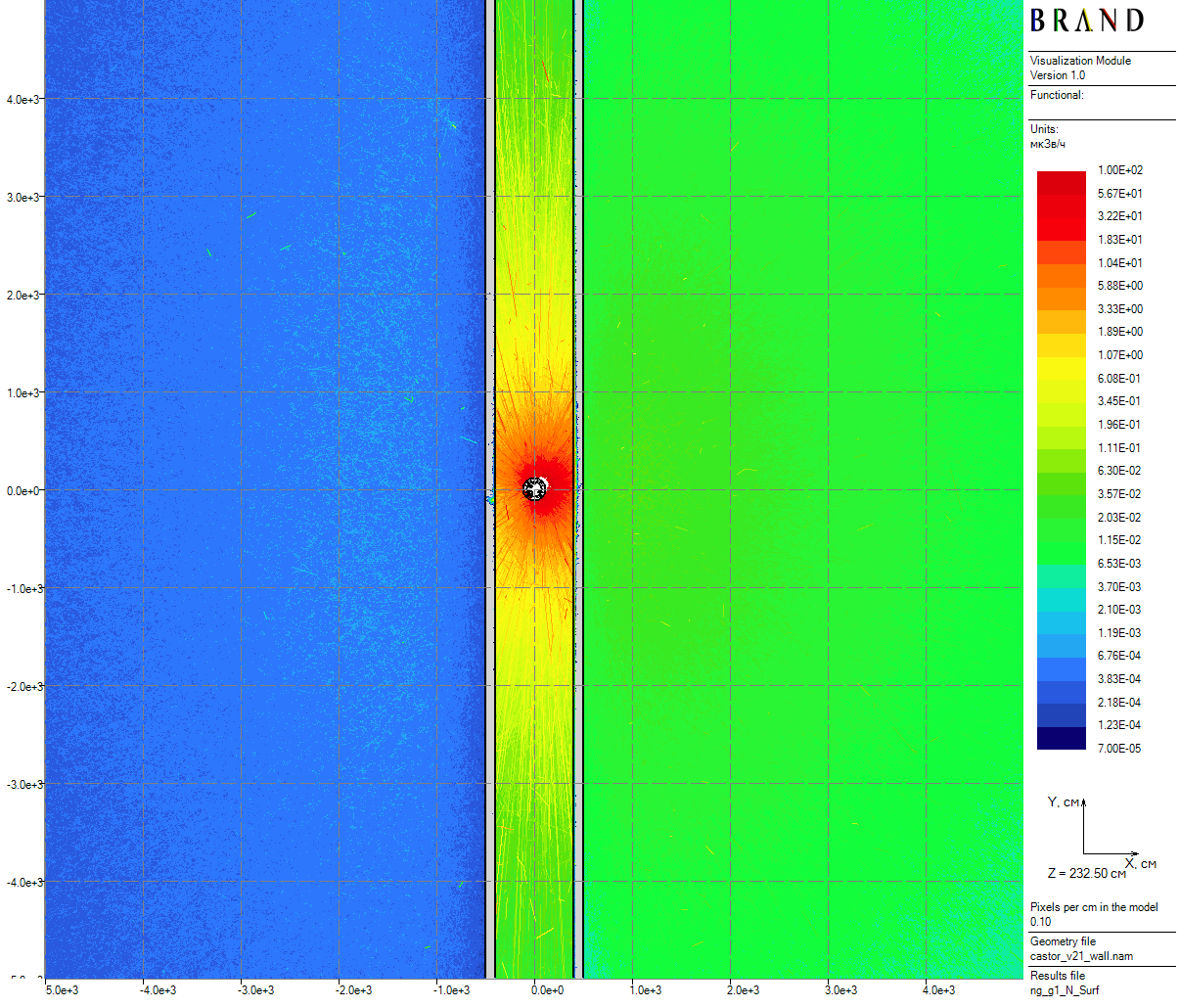 |
| Figure 7: Neutron horizontal dose rates for the cask in the skyshine model (50 cm thick) |
Primary gamma results
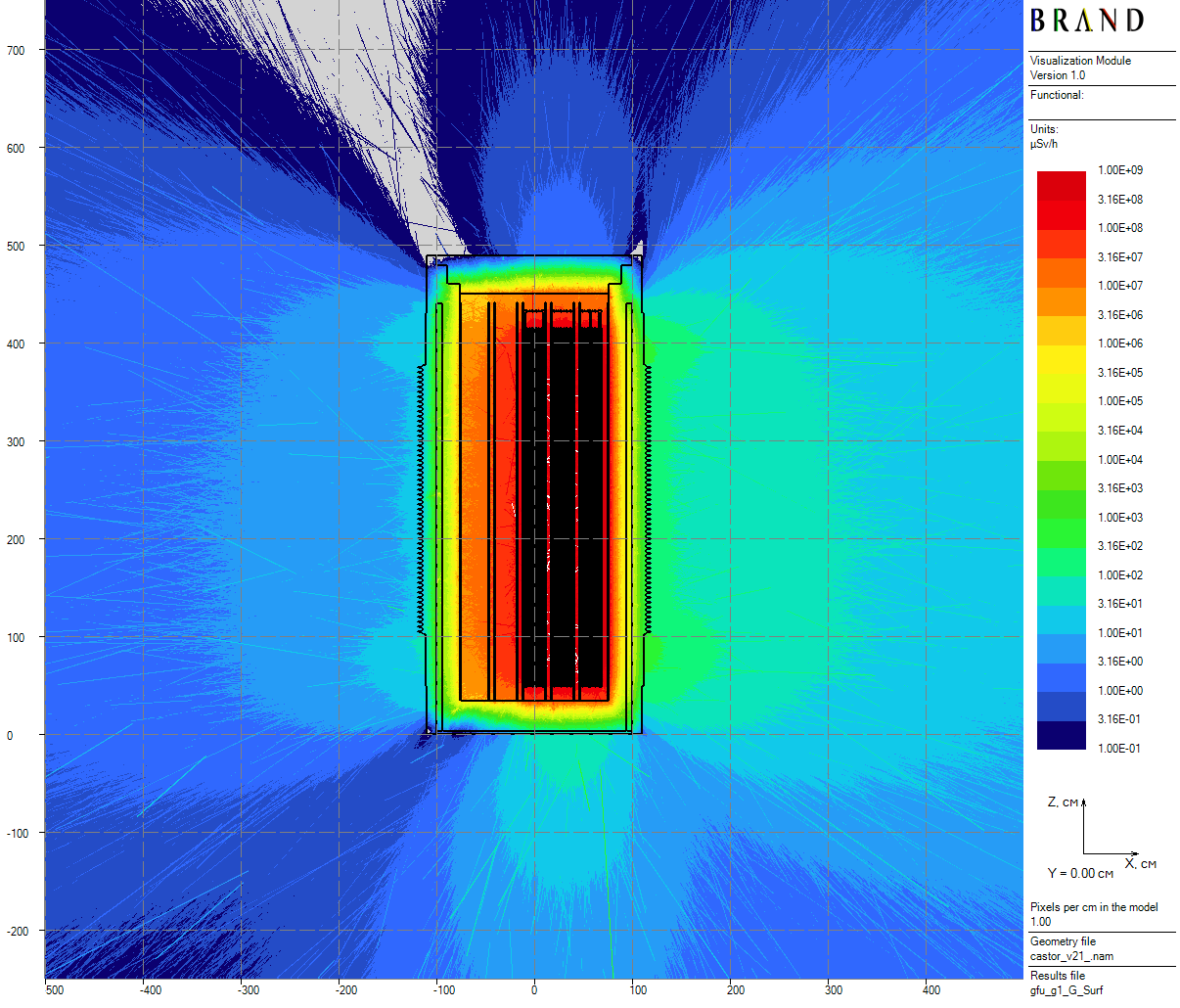 |
| Figure 8: Primary gamma axial dose rates for the single cask (20 cm thick) |
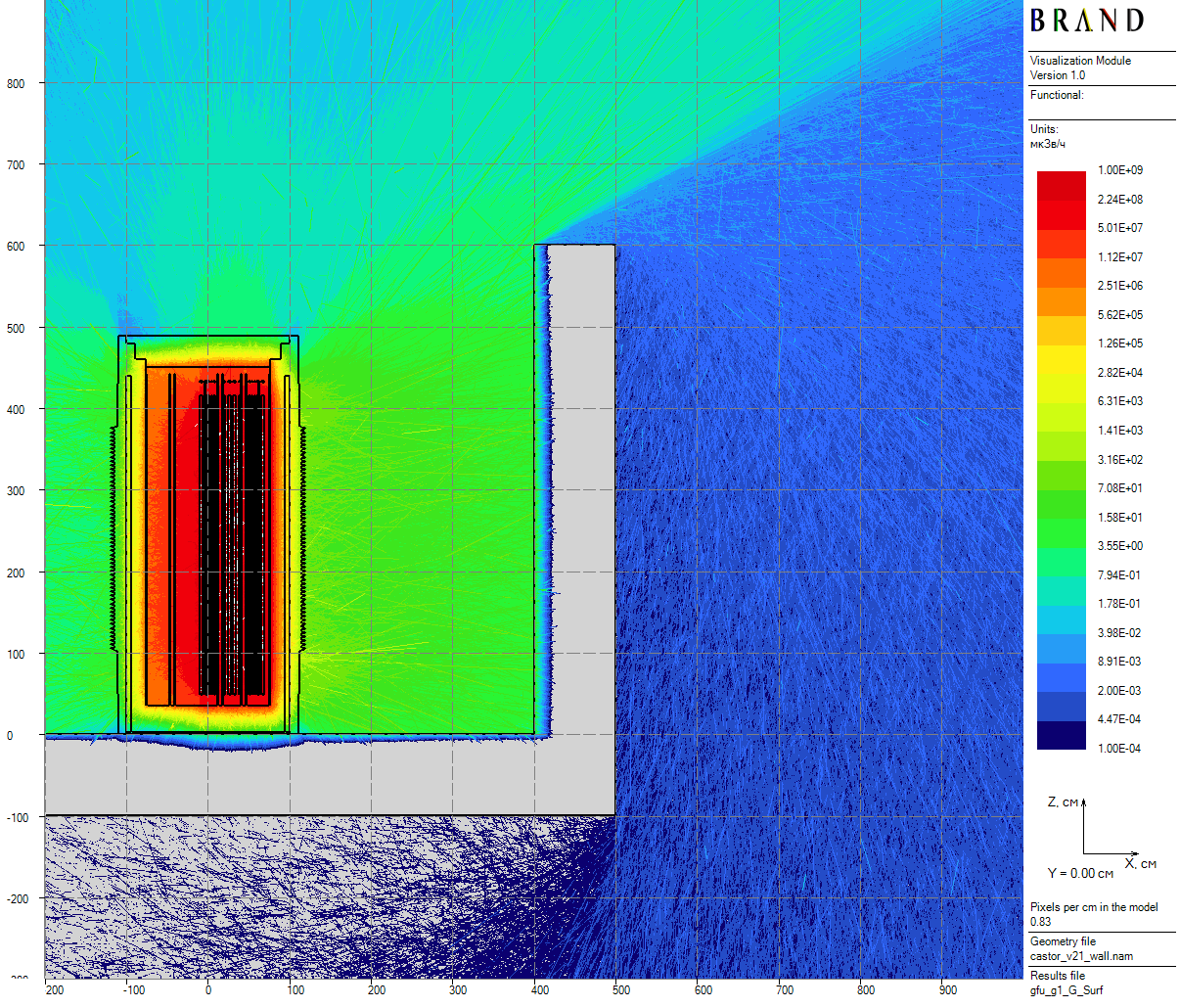 |
| Figure 9: Primary gamma vertical dose rates for the cask in the skyshine model (20 cm thick) |
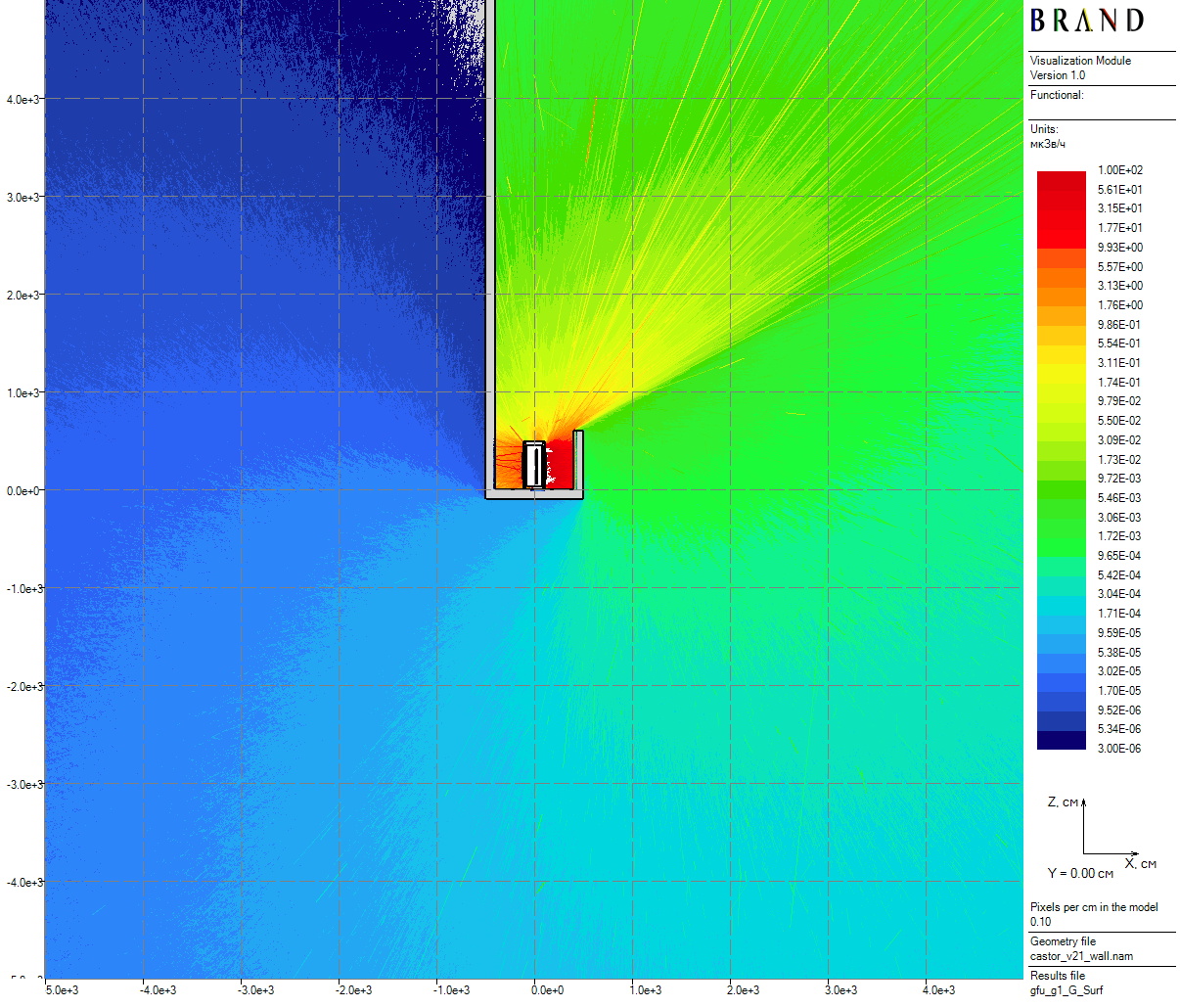 |
| Figure 10: Primary gamma vertical dose rates for the cask in the skyshine model (100 cm thick) |
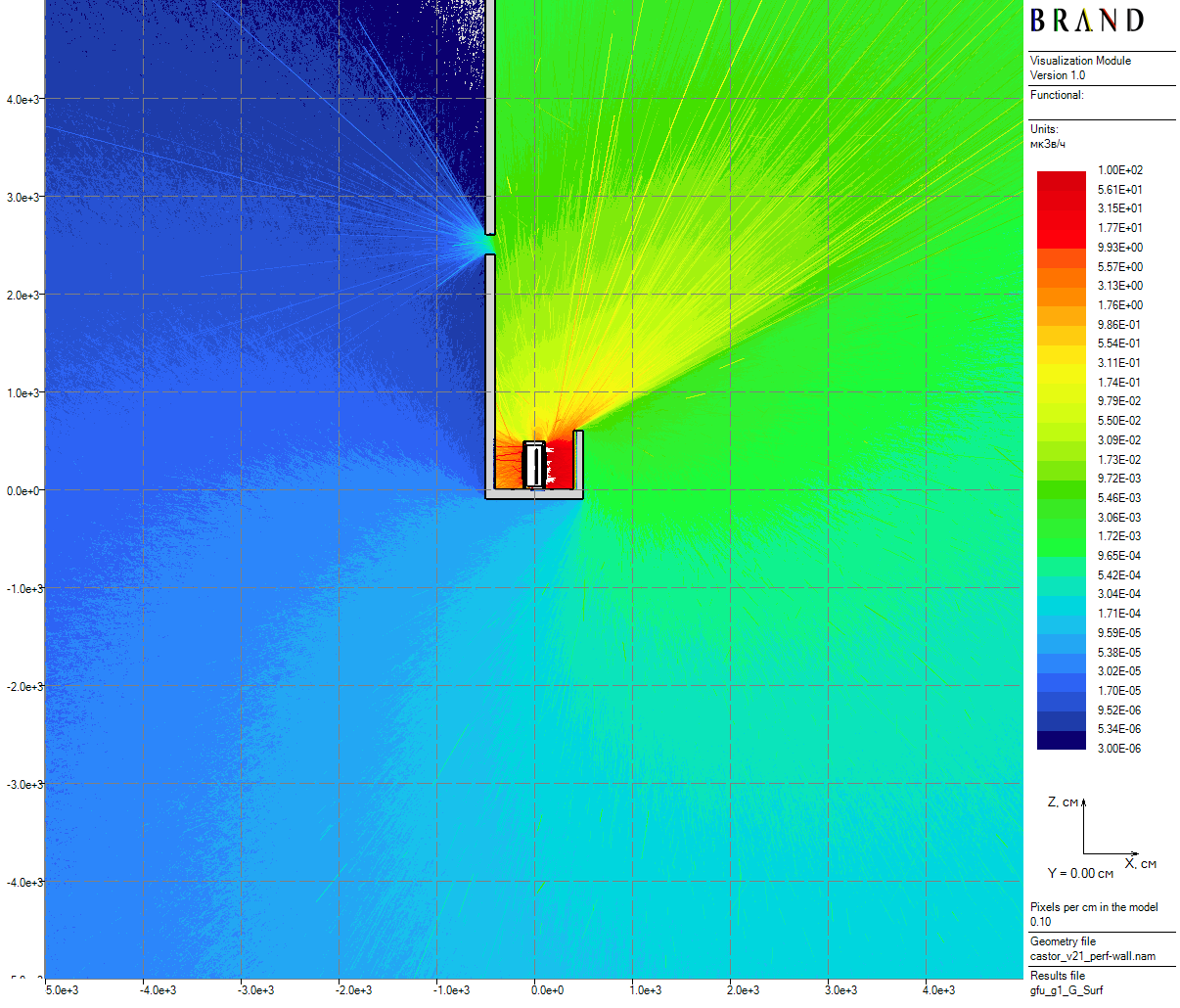 |
| Figure 11: Primary gamma vertical dose rates for the cask in the skyshine model with the perforation (100 cm thick) |
 |
| Figure 12: Primary gamma azimuthal dose rates for the single cask (20 cm thick) |
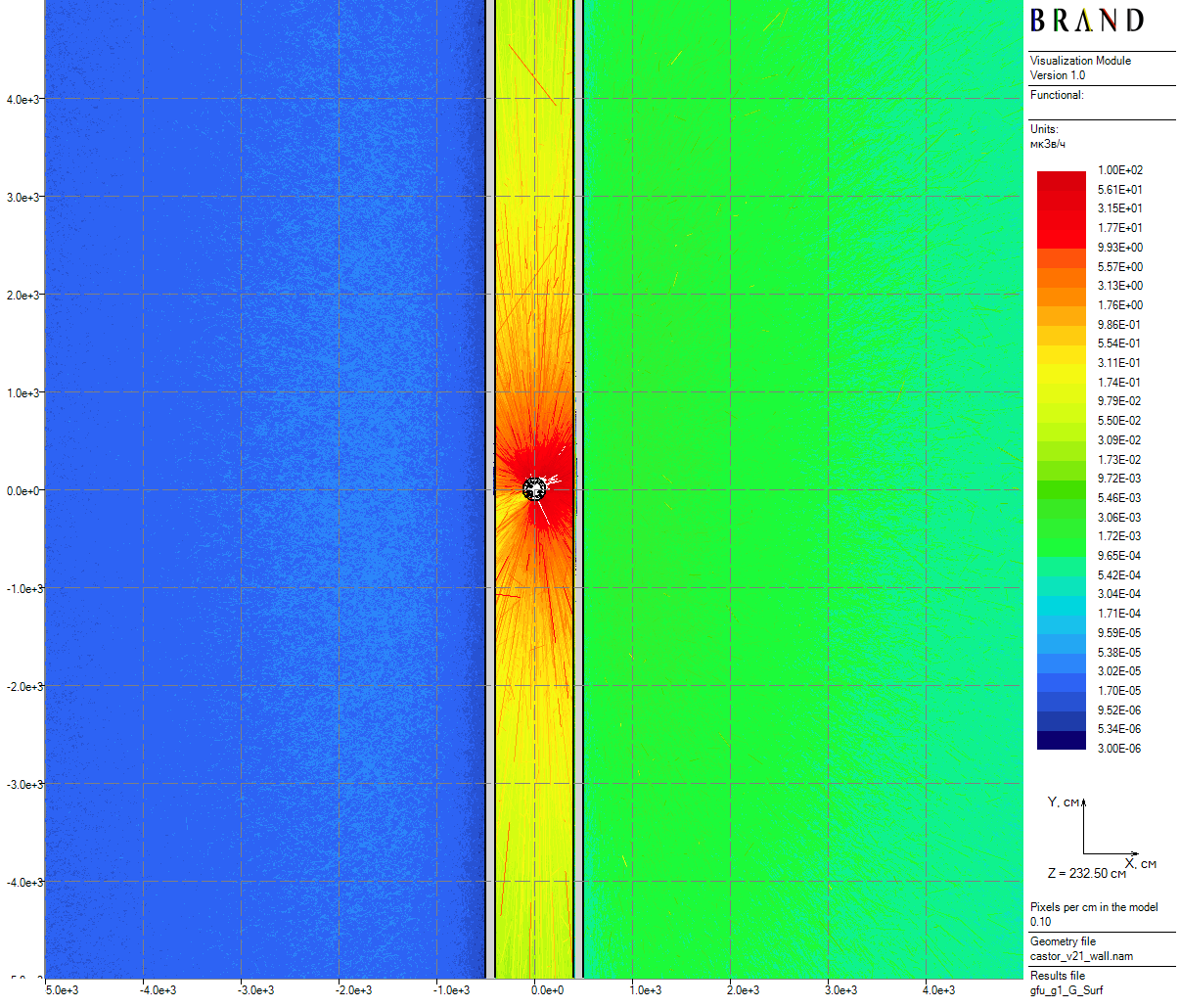 |
| Figure 13: Primary gamma horizontal dose rates for the cask in the skyshine model (50 cm thick) |
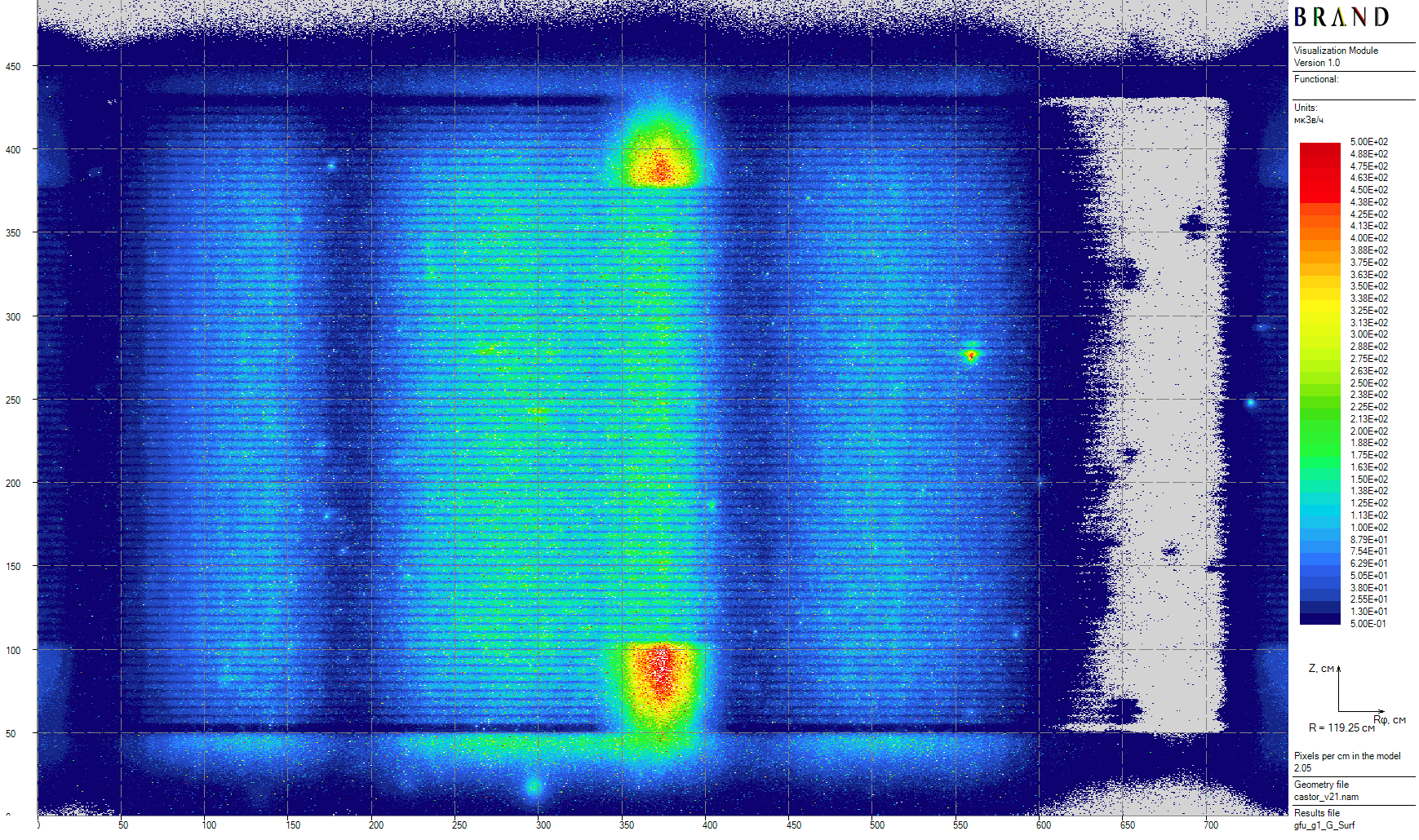 |
| Figure 14: Primary gamma side surface dose rates for the single cask (the extended calculation for 25.2 hours) |
Prev ….. Next
References
- B. L. Broadhead, J. S. Tang, R. L. Childs, C. V. Parks, and H. Taniuchi. Evaluation of shielding
analysis methods in spent fuel cask environments. Technical Report EPRI TR-104329, Oak Ridge
National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States), 1995.
- International Commission on Radiological Protection., International Commission on Radiation Units,
and Measurements. Conversion coefficients for use in radiological protection against external radiation.
Annals of the ICRP ; v. 26, no. 3/4. Published for the Commission by Pergamon Press, Oxford;, 1st
ed. edition, 1996 - 1997.
- V.G. Mogulian. An approach to radiation shielding evaluations using estimators by expected scoring. 2025. doi:10.5281/zenodo.16781416.
Copyright © 2025-2026 Vitaly Mogulian. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.













