Vitaly Mogulian
Monte Carlo Variance Reduction Research & Code Developing & Nuclear Engineering
| Research Profile | BRAND Shielding Evaluations | GitHub |
Concrete Anthill toy model
This model imitates a hypothetical large spent fuel dry storage. It has heterogeneous concrete shields including numerous labyrinths, rooms, and cavities of complicated configuration. An interesting feature of the designed problem is the relatively strong attenuation of dose rates for both neutrons and gamma radiation which magnitudes reach $10^{-15} - 10^{-19}$. In combination with a large heterogeneous self-shielded source, it makes this problem to be suitable for investigations of designed variance reduction techniques application to full-scale shielding evaluations.
The model is based on a regular $61 \times 61$ lattice of $25 \times 25 \times 410$ cm prisms. In the central $21 \times 21$ cells fragment, 441 PWR spent fuel assemblies from the CASTOR-V/21 model are placed. The remaining part of the model is a complex heterogeneous shield and its prisms are filled with either concrete or air (see Figure 1). In total, shield thicknesses in each side direction are equal to 500 cm but shield thickness of the monolite concrete slab in the top direction is 400 cm.
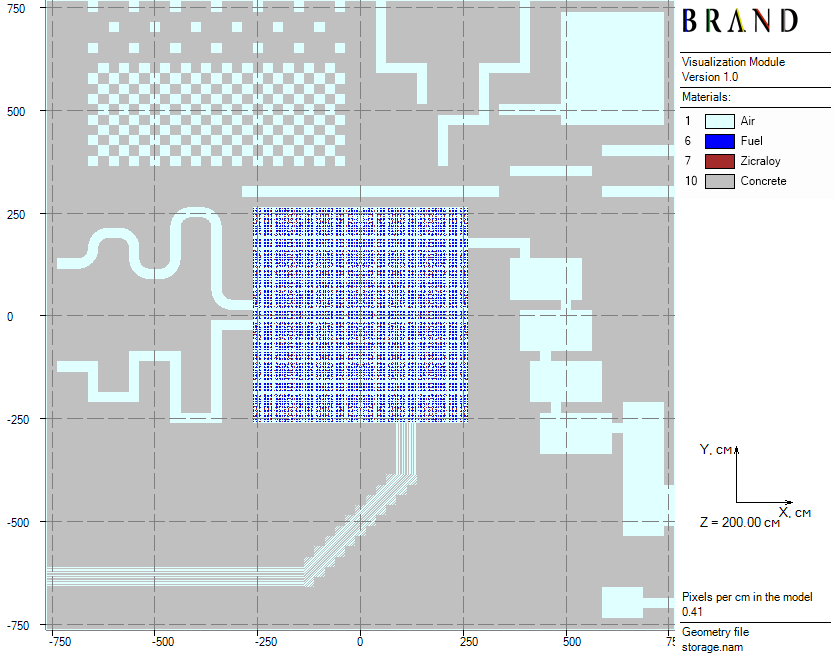 |
|---|
| Figure 1: Horizontal model cross-section |
In this calculation, the following techniques are used:
- Expected value estimators;
- Joint location-direction importance sampling for (for gamma only);
- Energy importance sampling for (for gamma only);
- Exponential transform;
- Simplified adaptive splitting.
The primary computational gain is achieved here thanks to the simplified adaptive splitting, joint location-direction IS (for primary gamma), and exponential transform techniques.
Computed flux functional - ambient equivalent dose H*(10) [1] rates, thickness of volumetric detectors are equal to 100 cm. Below, some results of neutron-gamma and gamma problems 24.3 hours long computation are presented (see details in [2]). Despite the smoothness of the plots, valid estimations seems to require $\times 10$ times larger statistics for enough precision.
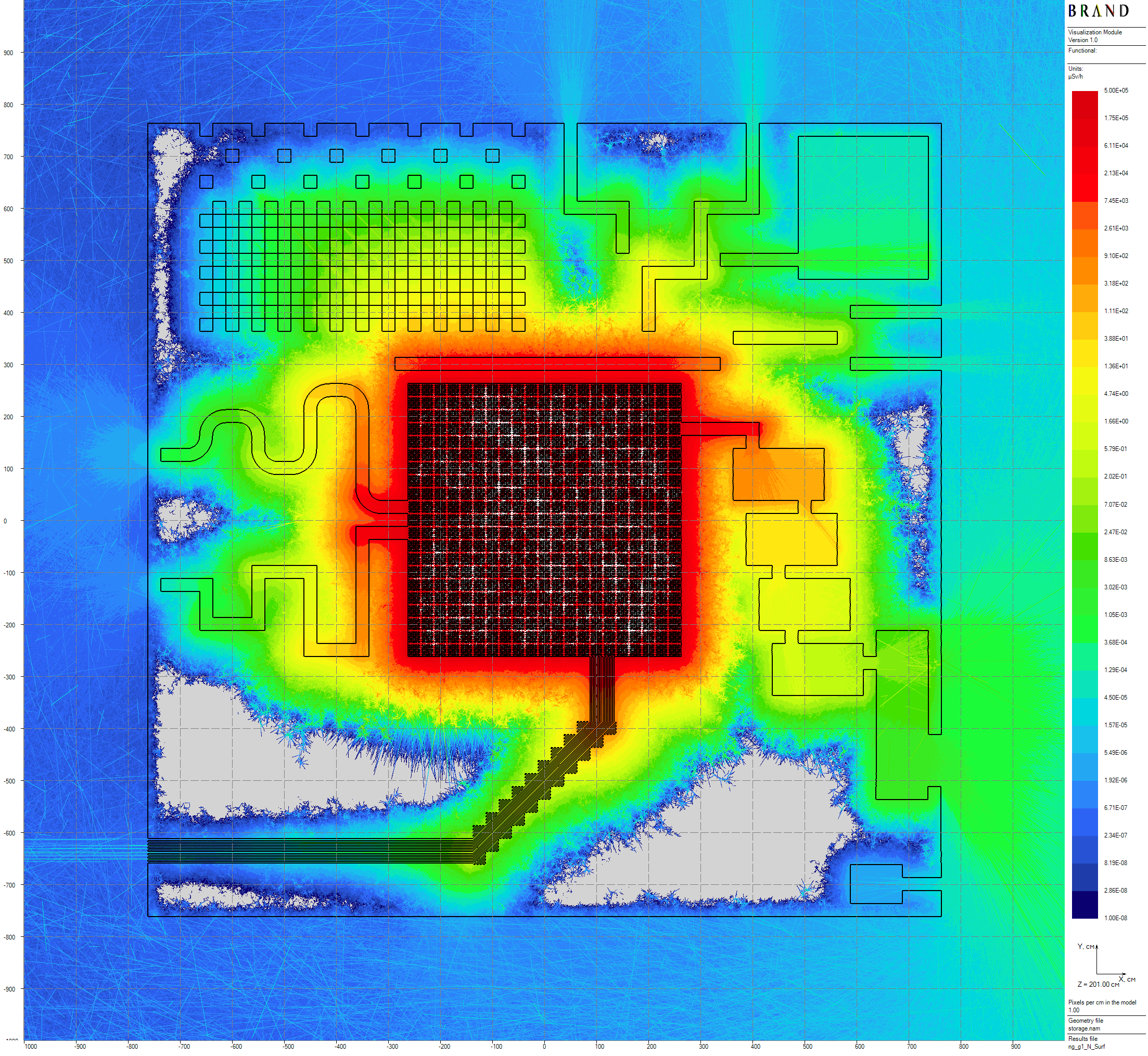 |
|---|
| Figure 2: Neutron horizontal dose rates distribution |
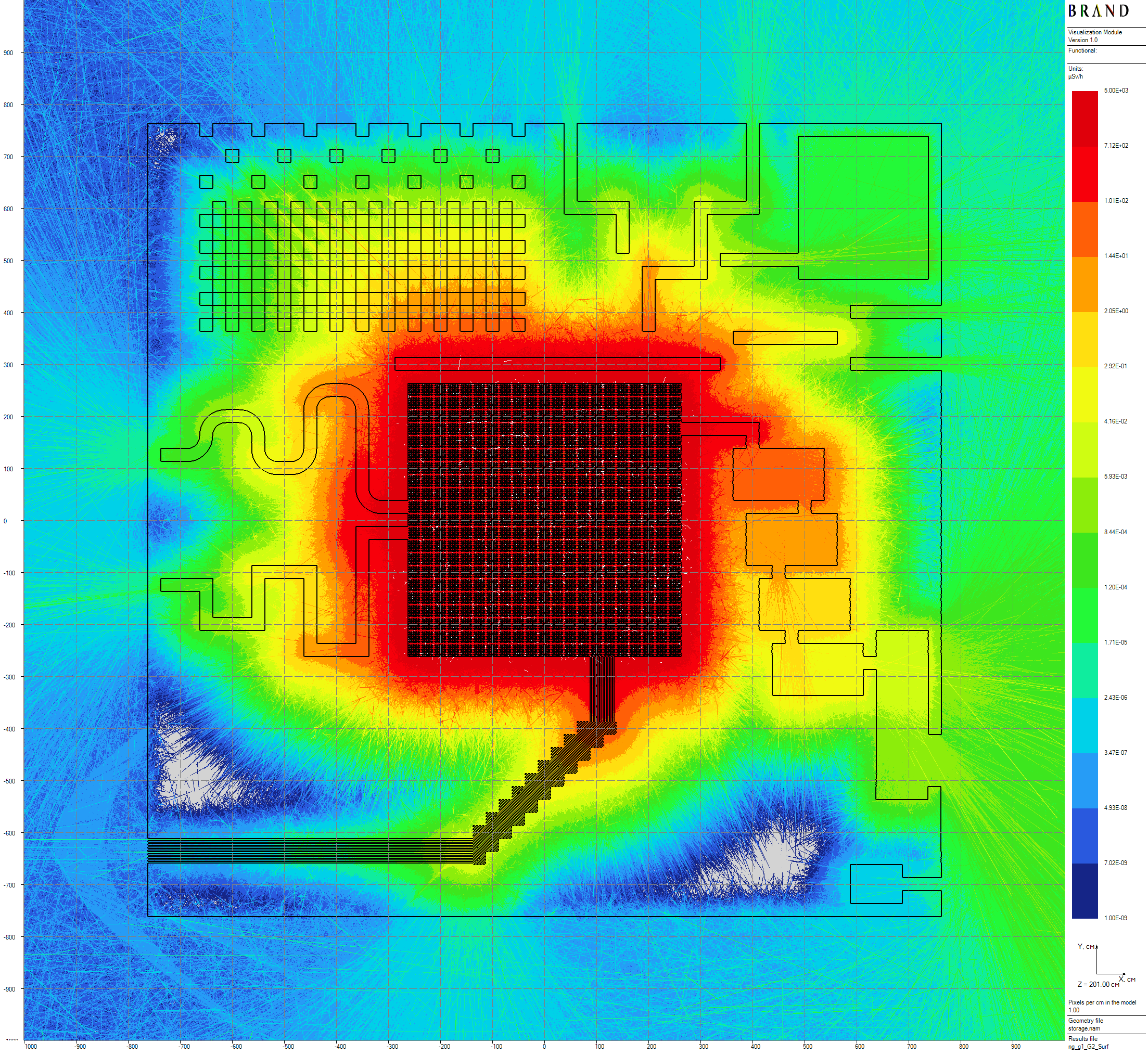 |
|---|
| Figure 3: Secondary gamma horizontal dose rates distribution |
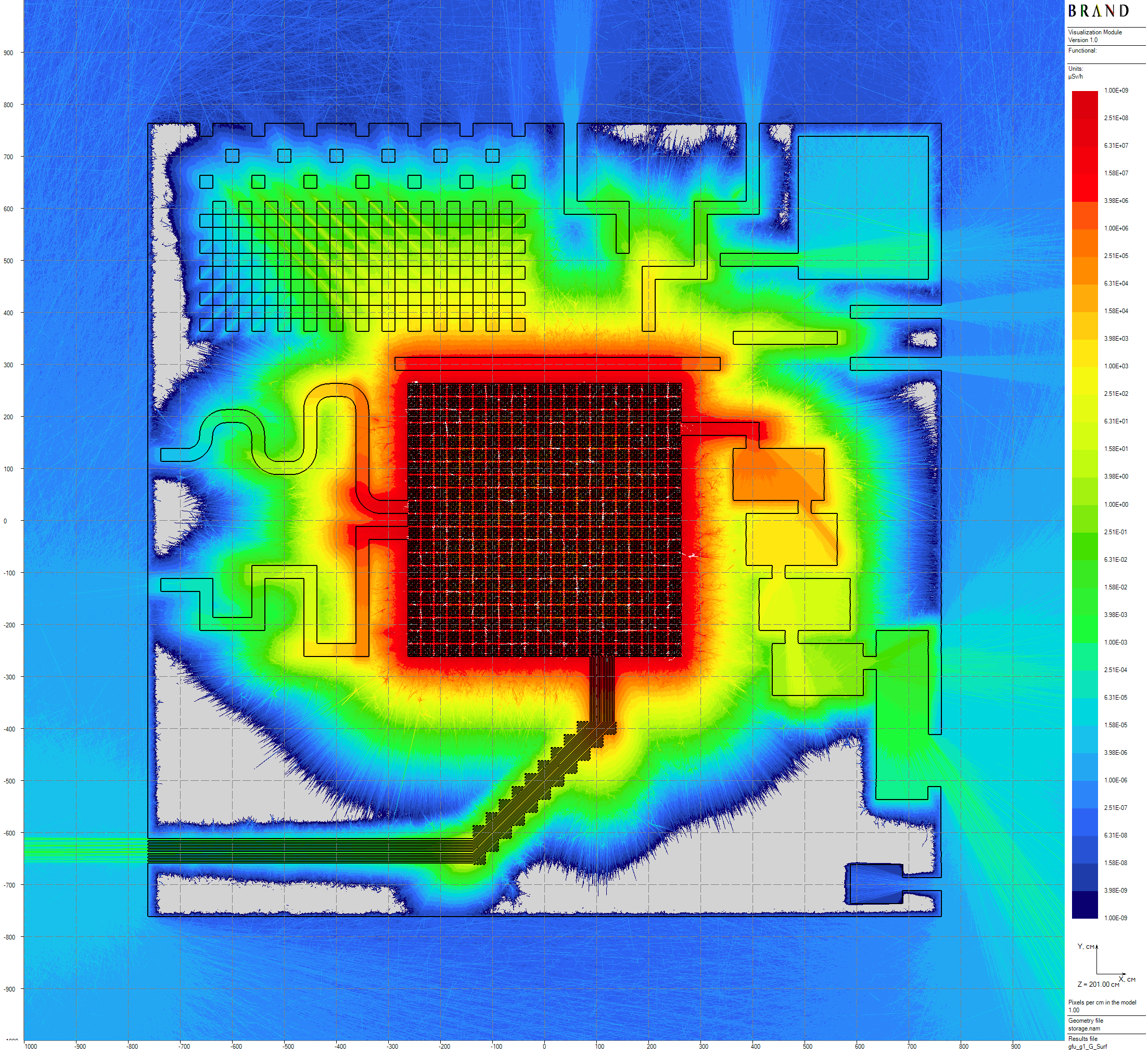 |
|---|
| Figure 4: Primary gamma horizontal dose rates distribution |
References
- International Commission on Radiological Protection., International Commission on Radiation Units, and Measurements. Conversion coefficients for use in radiological protection against external radiation. Annals of the ICRP ; v. 26, no. 3/4. Published for the Commission by Pergamon Press, Oxford ;, 1st ed. edition, 1996 - 1997.
- V.G. Mogulian. An approach to radiation shielding evaluations using estimators by expected scoring. 2025. doi:10.5281/zenodo.16781416.
Copyright © 2025-2026 Vitaly Mogulian. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.